|
|
||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|
|
||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|
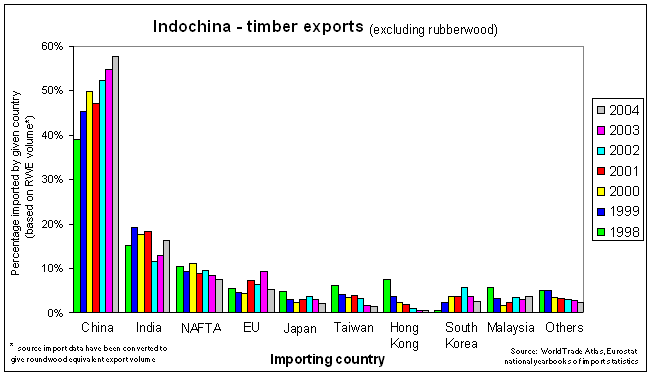
Indochina |
||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|
Imports of logs from Burma declared by China (Overland routes)
Imports of logs from Burma declared by China
(Other than by overland routes)
Imports of logs from Burma declared by India
|
||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|
China is the dominant influence on the region's remaining timber sector. Thailand, itself a major importer of the region's timber exports is also the leading exporter from the region. However, most of Thailand's timber exports comprise rubberwood (which should not be regarded as tropical timber). Thailand's exports have risen very rapidly since the late 1990s. Imports by China have led this increase. Thailand is the (initial) destination for the great majority of Laos's exports and used to be the dominant market for Cambodian timber exports. Burma is the region's second largest exporter. China, whose military and other assistance to Burma's junta has made Burma something of a vassal state to China, is the dominant import market, followed by India and Thailand. Local knowledge of how to manage Burma's teak forests sustainably is also disappearing. The junta has given local warlords carte blanche concerning forest exploitation in return for the elimination of opposition. China displaced Thailand as the principal market for Cambodian timber exports after the log export ban of 1995. Such has been Chinese importers' lack of concern for the provenance of Cambodian timber and the impunity with which Malaysian (mainly ethnic chinese) and Chinese companies have been allowed to log illegally that a ban on logging had to be introduced in 2002. In part because Cambodia's elite have chosen (/been persuaded) to manage their nation's assets as they have, the country's principal source of foreign exchange is now the international community. Failing to address illegal logging had previously led directly to cessation of all foreign aid. Howeve, the World Bank currently condones de facto forest management in Cambodia Vietnam is one
of the world's leading suppliers of wooden garden furniture (a niche
product which, because manufacturing costs are so low in this part
of the world, is increasingly targeted at the mass market). Having
until recently been closed to Vietnamese exports, the USA is now a
major potential market for Vietnam's export-oriented timber sector.
Much of the wood raw material is imported - some illegally, some from
FSC-certified sources. |
||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|
Copyright
globaltimber.org.uk
|
||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||